Short Course in Naples (Sept. 11), EAGE NSG Presentation (Sept. 10), New Article, Examples and Case Studies in Manuals
1. SHORT COURSE on Surface Wave Analysis: Solving Ambiguities and Pitfalls through Multi-Component Data (3C Nodes) – Sept. 11, 2025, Naples, Italy
2. PRESENTATION at the EAGE NSG Conference – Sept. 10, 2025, Naples, Italy
3. NEW ARTICLE on Possible Effects of Industrial Components on the Miniature Array Analysis of Microtremors and Horizontal-to-Vertical Spectral Ratio
4. Examples and case studies in winMASW®, HS® and ELIOVSP® manuals
1. FREE SHORT COURSE: Surface Wave Analysis: Solving Ambiguities and Pitfalls through Multi-Component Data (3C nodes) – Naples, September 11, 2025
Date: September 11, 2025
Time: 14:00 – 18:00 Rome time (CEST) -> 12:00 – 16:00 UTC
Language: English
Speaker: Giancarlo Dal Moro
Location: Via Stendhal 23 – 80133 Naples, Italy [Hosted at the headquarters of the Order of Geologists of Campania]
Format: In-person (limited seats) or Online
Programme available HERE
Surface-wave and vibration data analysis have become essential tools in engineering, geotechnical and seismic hazard studies. However, the most popular techniques are often based on oversimplifications or misconceptions, which can lead to erroneous assessments of subsurface conditions or structural behavior.
This seminar provides both a theoretical foundation and practical guidance on key aspects critical to accurate and effective seismic and vibration data acquisition and analysis.
Participants will explore how to overcome common challenges in data acquisition and processing, and how to enhance their results through the analysis of multi-component data, in particular from 3-component (3C) nodes.
The course includes real-world case studies to reinforce learning through practical examples.
A dedicated discussion and Q&A session will provide space for questions, in-depth clarifications, and the exchange of experiences among participants.
To register, please send an email to info@winmasw.com including:
-
Full name(s) of participant(s)
-
Company, University or Research Organization
-
Attendance mode: In-person or Online
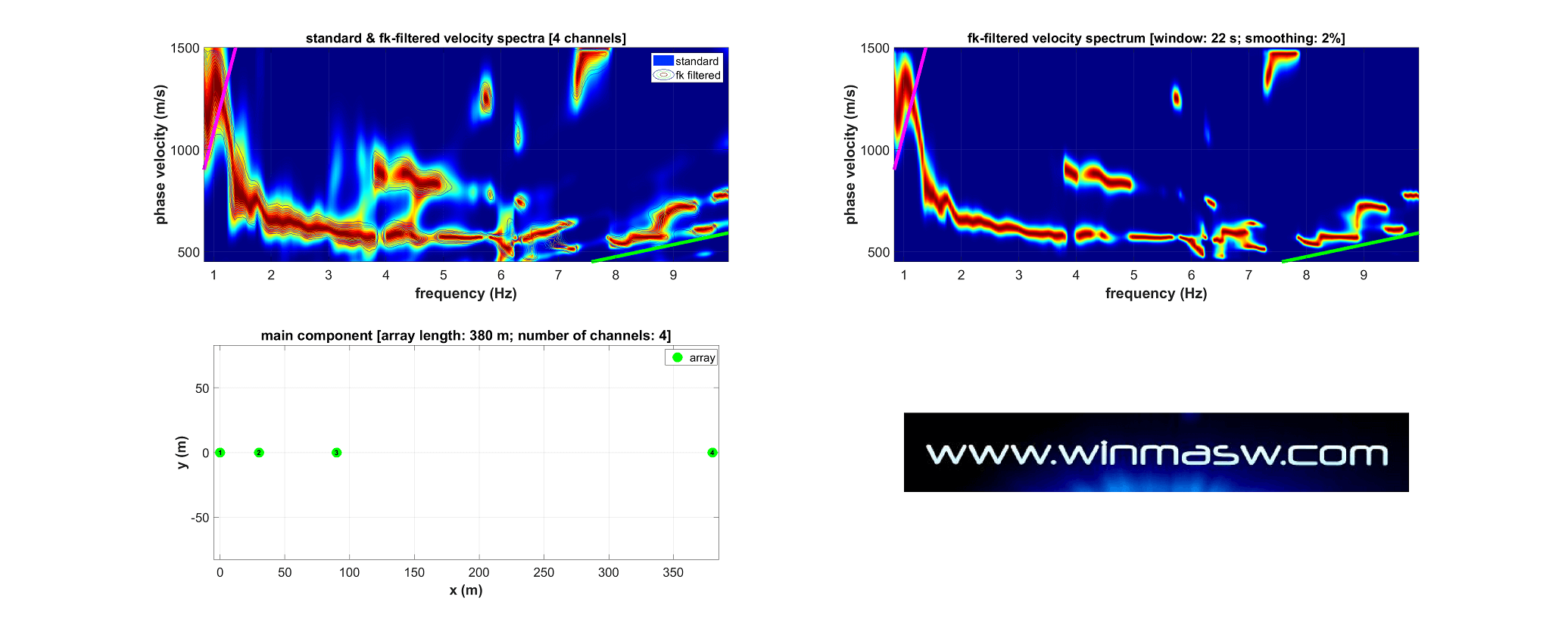
winMASW® Academy: multi-component ESAC using only 4 nodes with an array length of 380 meters
2. PRESENTATION at the EAGE NSG (European Association of Geoscientists and Engineers – Near Surface Geoscience) Conference, Naples (Italy)
Date and Time: September 10, 2025 | 11:10 – 11:30 AM
Venue: Stazione Marittima, Naples, Italy
Presentation Title: Efficient and Comprehensive Seismic Characterization of Peat-Rich Areas via Surface-Wave Analysis

3. NEW ARTICLE on Pure and Applied Geophysics
Pure and Applied Geophysics (Dal Moro, 2025)
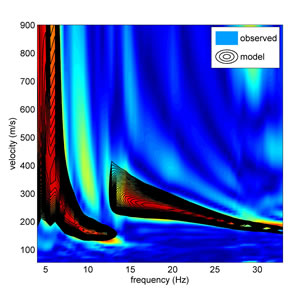
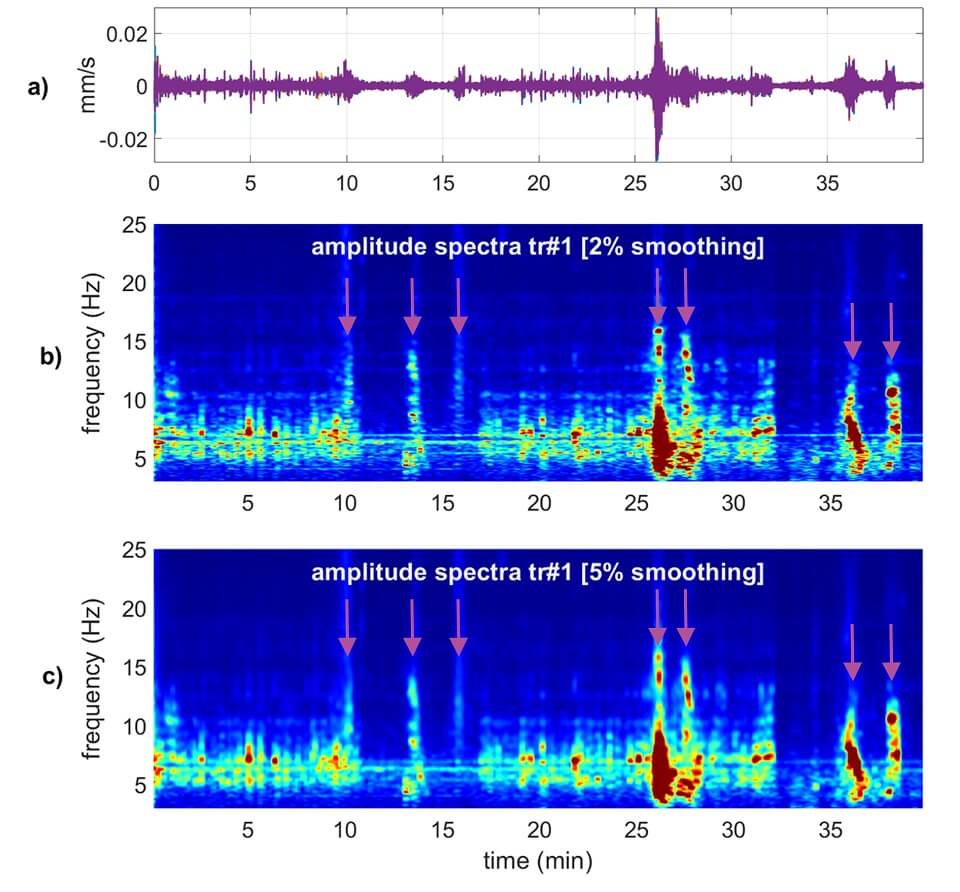
ABSTRACT. Surface-wave analysis can be performed according to a multitude of approaches. In fact, both the determination of the dispersive properties and data inversion can be accomplished according to several possible techniques, which should be chosen on a case-by-case basis, depending on the goals and site characteristics. The Miniature Array Analysis of Microtremors (MAAM) is an interesting methodology aimed at extracting the dispersive properties of the vertical (Z) component of Rayleigh waves from passive data recorded according to a circular-symmetry array. Compared to other techniques, MAAM can investigate larger wavelengths and provide phase velocities in a wider frequency range (a triangular array with a radius of a couple of meters can provide the dispersion curve in the 2-20 Hz frequency range, approximatively). Despite its remarkable potential, MAAM can be affected by industrial noise that alters the natural microtremor field. The comparative analysis of the Z component dispersion retrieved via Extended Spatial AutoCorrelation (ESAC) and MAAM is initially conducted to validate the adopted procedures and verify the paradigms to adopt to identify the frequency range properly investigated. Following this, analysing a second time-lapse dataset, the effects of industrial components on both the dispersion curve obtained via MAAM and the Horizontal-to-Vertical Spectral Ratio (HVSR) are investigated. The experimental evidences show that non-monochromatic industrial components can have a malicious effect on both MAAM and HVSR. In this context, analysing the coherence functions of the multi-component data recorded by a 3-component geophone, together with the spectral ratio and noise-to-signal ratio obtained during MAAM processing, is crucial for assessing the possible presence of industrial components that may affect the observables ultimately used in the joint inversion.
4. Examples and case studies in winMASW®, HoliSurface® and ELIOVSP® manuals
• winMASW®: MANUAL PDF
Appendix F – A Few Examples (Case Studies) of What You Can Do with winMASW®
• HoliSurface®: MANUAL PDF
Appendix H – A Few Examples of What You Can Do with HoliSurface® (Twelve Commented Case Studies)
• ELIOVSP® (DownHole seismics): MANUAL PDF
Chapter 8 – Examples of Data Processing
Remember that several articles are available HERE
- NEWS ARCHIVE
- share: